Internet Of Things
We are happy to show our company
What is the Internet of Things?
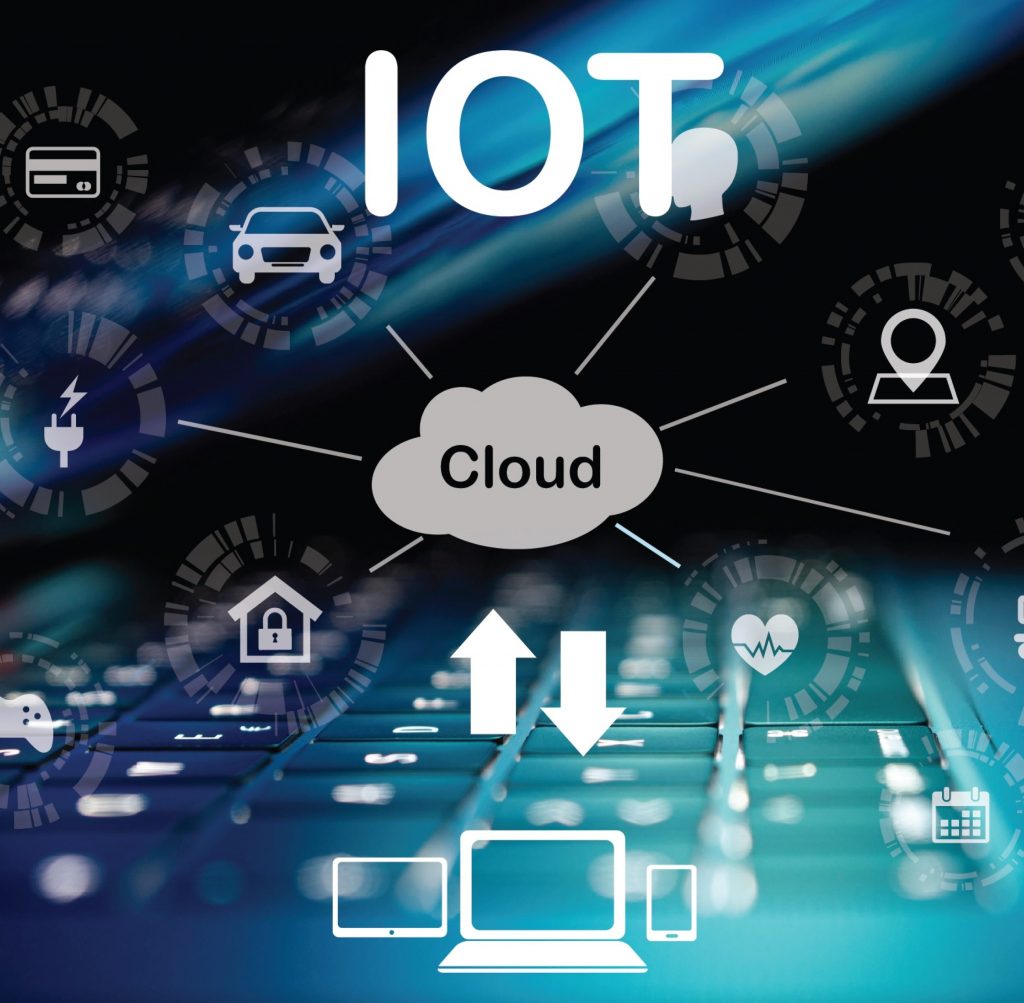
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the concept of a computational network of physical objects (“things”) equipped with embedded technologies for interacting with each other or with the external environment, excluding from the part of actions and operations the need for human participation.
We are introducing a new revolutionary Internet Of Things solution for you. Gambit Technology’s gateway resides inside your equipment and provides all IoT functionality with minimal efforts.
The History of Internet of Things in Electronic Design
In 1926, Nikola Tesla in an interview for Collier’s magazine said that in the future the radio will be transformed into a “big brain”, all things will become part of a whole, and the tools that make this possible will easily fit in your pocket. In 1982, a modified Coke vending machine at Carnegie Mellon University became the first network-connected appliance. In 1990, a graduate of MIT, one of the fathers of the TCP / IP protocol, John Romkey with Simon Hackett connected the first appliance (a toaster) to the internet.
The term “Internet of Things” was coined by Kevin Ashton in 1999. In the same year, the Auto-ID Center was established, which deals with radio frequency identification (RFID) and sensor technologies, thanks to which this concept has become widespread. By 2008-2009, there was a transition from the “Internet of people” to the “Internet of things”, i.e. the number of items connected to the network exceeded the number of people. As well as becoming commonplace in electronic design services, the development of IoT has gained traction among many application design services.
IoT Components
Devices included in the Internet of Things are any stand-alone devices connected to the Internet that can be monitored and/or controlled remotely. There are devices which transform information about the external environment into machine-readable data. A wide class of measuring instruments is used, from elementary sensors (for example, temperature, pressure, illumination), consumption metering devices (such as smart meters) to complex integrated measuring systems.
With the comprehensive dissemination of the “Internet of things”, it is important to ensure the uniqueness of object identifiers. There are a lot of methods for the automatic device identification: RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) tags, machine-readable barcode or QR code symbols, MAC address, RTLS (Real-Time Location Systems).
A layer of Internet communications that allows operators to communicate with the device, and devices communicate with each other. These are the connection methods. The range of possible data transfer technologies covers all possible means of wireless and wired networks (for example ZigBee, Wireless HART (wireless sensor networking technology based on the Highway Addressable Remote Transducer Protocol) , Wi-Fi, LPWAN (Low-Power Wide-area Network)).
There are applications which include protocols, interfaces that devices use to identify and communicate with each other, data processing tools. Received data should be collected, analyzed and further used to make business decisions. Dashboard panels allow people to use IoT devices by connecting to them and controlling them by means of the smartphones, tablets, PCs, smartwatches, televisions and non-traditional remote controls.
Software systems that analyze data received from IoT devices. Analytics is used in a large number of scenarios, for example, to predict maintenance.

How Can The Internet of Things Benefit Industries?
- City transport with displacement sensors
- Garbage cans with filling sensors
- Planning of transport routes based on data on the movement of people around the city
- Video surveillance
- Sensors in the ground indicate the soil conditions (moisture, plant nutrition)
- Drones evaluate crop health, crop growth, and pest attack
- Neural networks can help engineers assess soil conditions
- Department stores without cashiers
- Cameras that recognize the emotions of customers
- Sensor located in each shelf sends notification if any products are out of stock


- City transport with displacement sensors
- Garbage cans with filling sensors
- Planning of transport routes based on data on the movement of people around the city
- Video surveillance
- Sensors in the ground indicate the soil conditions (moisture, plant nutrition)
- Drones evaluate crop health, crop growth, and pest attack
- Neural networks can help engineers assess soil conditions
- Department stores without cashiers
- Cameras that recognize the emotions of customers
- Sensor located in each shelf sends notification if any products are out of stock
- Wearable Body Area Sensors connected to smart phones
- Medical devices connected to the Internet can predict a risk heart attack (for example Blood pressure tools in the Shopper Drug marts)
- Temporary pacemakers allow the doctors to monitor and control heart bits of the patients
- Video surveillance and security systems are becoming part of the life of both individual businesses and entire cities
- Cameras with face recognition in the subway are the Internet of things
- Surveillance cameras can detect and capture an image of traffic rules violator, and monitoring authority can take proper steps
- It provides an extra facility to the ambulance
- Less human effort to manage traffic system
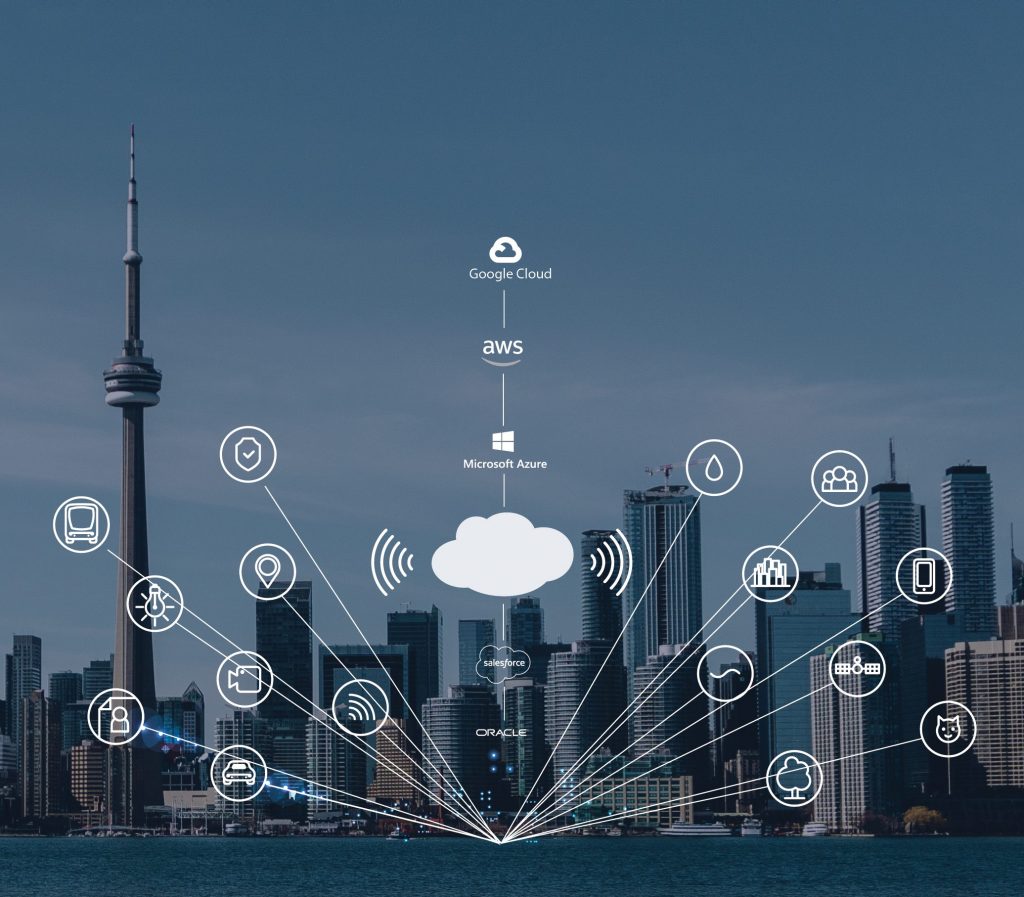

Main IoT Platform Companies
IoT platforms serve as a bridge between device sensors and the data network. IoT platform is the support software that connects edge hardware, access points, and data networks to other parts of the value chain (which are generally the end-user applications). The followings are some of the largest IoT platforms currently operating in this market:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- ThingWorx IoT Platform
- IBM’s Watson
- Cisco IoT Cloud Connect
- Salesforce IoT Cloud
- Oracle Integrated Cloud
- GE Predix -Google Cloud Platform
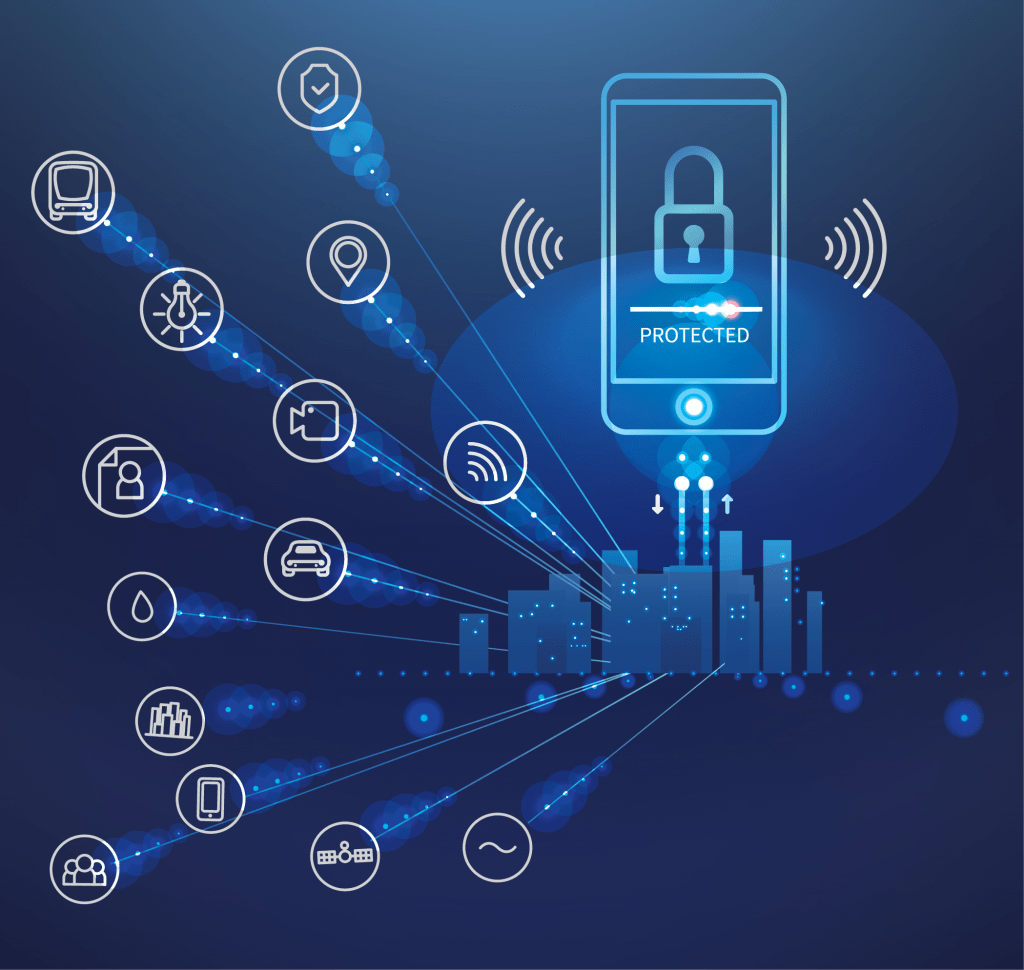
Problems with The Internet of Things
Every linked tool creates opportunities for cyber-attackers. Potentially, the IoT is a wealth of information about those who use it. For this reason, having a secure internet of things design methodology is essential for protecting users of IoT-enabled devices and applications. Here are several serious cases of IoT hacking and cyberattacks in recent history:
This IoT botnet was made possible by malware called Mirai. Once infected with Mirai, computers continually search the internet for vulnerable IoT devices and then use known default usernames and passwords to log in, infecting them with malware. These devices were things like digital cameras and DVR players
The devices, like pacemakers and defibrillators, are used to monitor and control patients’ heart functions and prevent heart attacks. The vulnerability occurred in the transmitter that reads the device’s data and remotely shares it with physicians.
The IBM security intelligence website reported the Jeep hack a few years ago, saying, “It was just one, but it was enough. In July [2015], a team of researchers was able to take total control of a Jeep SUV using the vehicle’s CAN bus. By exploiting a firmware update vulnerability, they hijacked the vehicle over the Sprint cellular network and discovered they could make it speed up, slow down and even veer off the road. It’s proof of concept for emerging IoT hacks: While companies often ignore the security of peripheral devices or networks, the consequences can be disastrous.”
The IoT consists of a lot of individual devices with their own specifications. At this stage, that hardly matters, but a time will arrive soon when further growth will require that smart devices can communicate with each other.
A challenge for producers of IoT applications is to process and interpret the vast amount of data which is gathered by the sensors. Thirty or more billion devices, which are predicted to be connected to the Internet in 2020, will generate 44 billion terabytes of data. This is about seven times the amount of digitized information worldwide as of the 2010. Therefore, application design services need to be conscious of their responsibility in storing and protecting data belonging to the public.
- BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) is more suitable for the wearable devices
- Wi-Fi communications are applied for smart homes and offices.
- Industrial Ethernet is used for factories and plants for long time
- Mobile technology (4G) is proper to smart cities and agriculture
- LPWAN networks are employed for energy efficiency applications
The Future of IoT in Electronic and Application Design Services
A new term has already appeared: The Internet of Everything (IoE). This will soon replace the Internet of Things and further revolutionize electronic design services and application design services across the planet. At Gambit Technology, we strive to stay at the helm of innovation in electronic design, including with our IoT development and design services. We have recently launched an upcoming IoT project called IoT Links. This project will enable users to easily control all of Arshon’s devices in one application. Visit IoT Links to learn more.